Iron Regulation Information
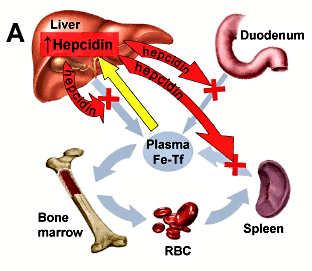
A. The role of hepcidin in normal iron homeostasis: an increase in plasma iron causes an increase in hepcidin production (yellow arrow). Elevated hepcidin inhibits iron flow into the plasma from macrophages, hepatocytes and the duodenum. As the plasma iron continues to be consumed for hemoglobin synthesis, the plasma iron levels decrease and hepcidin production abates, completing the homeostatic loop.
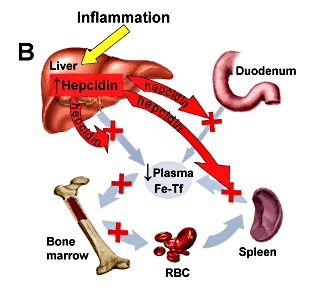
B. The role of hepcidin in anemia of inflammation: IL-6 and other cytokines induce hepcidin production (yellow arrow). Increased concentrations of hepcidin inhibit iron efflux from macrophages, from hepatic storage and from the duodenum into plasma. Hypoferremia develops, and erythropoiesis becomes iron-limited.
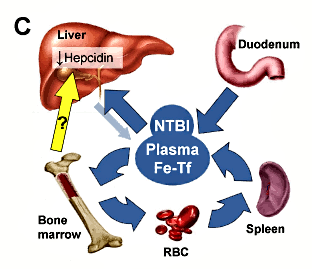
C. The role of hepcidin in iron-loading anemias: greatly increased erythropoietic drive suppresses hepcidin production through as yet undefined pathway(s) (yellow arrow). Low hepcidin allows excessive iron absorption, leading to increased plasma iron levels, elevated transferrin saturation and accumulation of non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI). Hepcidin regulation by iron remains blunted because of the dominating erythropoietic signal resulting in excessive iron loading, deposition of iron in vital organs and organ damage.
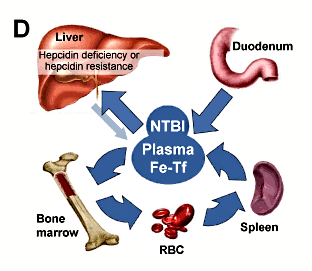
D. The role of hepcidin in hereditary hemochromatosis: hereditary hemochromatosis is caused either by hepcidin deficiency or hepcidin resistance. Hepcidin deficiency is caused by mutations in the hepcidin gene or genes encoding hepcidin regulators. Hepcidin resistance is a rare form of hereditary hemochromatosis and results from mutations in hepcidin’s receptor/iron channel ferroportin. Low hepcidin or the lack of hepcidin effect due to resistance allows excessive iron absorption, leading to increased plasma iron levels, elevated transferrin saturation and accumulation of non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI). Excess iron is deposited in vital organs and causes organ damage.